-
Clearing & Settlement and Redressal
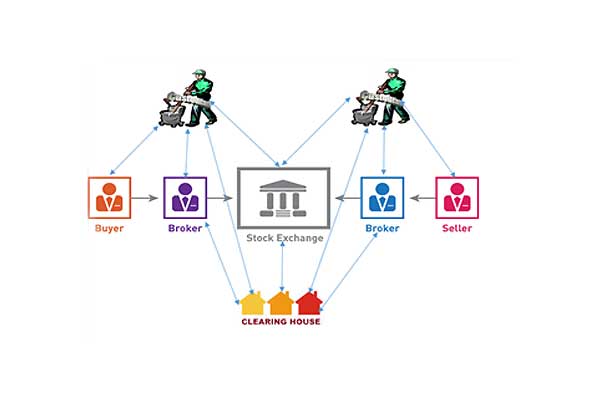
What is a Clearing Corporation?
A clearing corporation is a part of an exchange and performs three functions, namely,
- It clears and settles all transactions i.e. complete the process of receiving and delivering shares/funds to the buyers and sellers in the market.
- It provides financial guarantee for all transactions executed on the exchange
- Provides risk management functions.
National Securities Clearing Corporation Limited (NSCCL), a 100% subsidiary of NSE, performs the role of a clearing corporation for transactions executed on NSE.
-
What is Rolling Settlement?
Settlement is the process whereby payment is made by the buyers, and shares are delivered by the sellers. Rolling Settlement is a mechanism of settling trades done on a stock exchange on T i.e. trade day plus "X" trading days, where "X" could be 1,2,3,4 or 5 days.
In India, we have adopted the T+2 settlement cycle. This means that a transaction conducted on Day 1 has to be settled on the Day 1 + 2 working days. This is when funds are paid and securities are transferred. Thus, 'T+2' here, refers to Today + 2nd working day.

-
What is Pay-in and Pay-out?
Pay in is where the brokers shall make payment of funds or delivery of securities to the exchange. Pay out day is the day when the exchange makes payment of funds or delivery of securities to the broker
Transaction Buyer Seller Pay In (T+1) Funds are delivered Shares are delivered Pay out (T+2) Shares are Received Funds are received 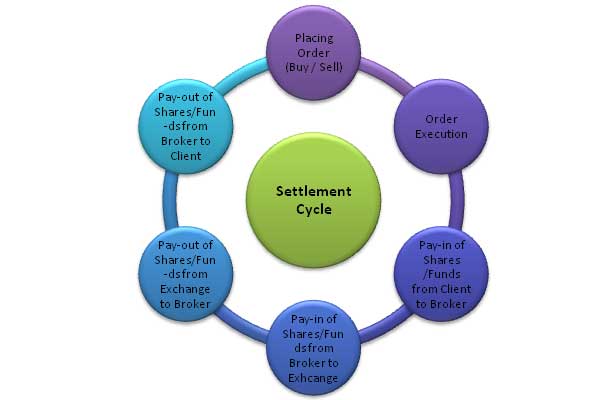
-
What is Trade for Trade settlement?
Trade for Trade or T segment is a segment in which no intra-day trading is allowed for shares falling in that segment, as each trade results in delivery. Transactions placed in this segment have to be mandatorily settled either by taking or giving delivery even if you have bought and sold the shares during the same settlement cycle.
In simple words, Trade for Trade segment tells that, if you buy shares you must pay the money and take delivery. Similarly, if you sell shares, you must give the delivery of shares and you will get money. On the other hand, if you buy today and sell today and don‘t have delivery, then the sell position will go in to auction. Generally illiquid stocks come under this category.

-
What is an Auction?
Auctions are conducted on exchange when, for some reason, shares are not delivered by the seller to the exchange on time. Hence, the exchange purchases the necessary quantity in the auction market and gives them to the trading member. The shortages are met through auction process and the difference in price indicated in the contract note and price received through auction is paid by the seller to the exchange, which is then liable to be recovered from the client.
What is an auction close out?
Close out is effected for the cases when no offer for a particular security is received in an auction or when members who offer the securities in auction, fail to deliver the same or shortages pertaining to those groups of securities for which auctions are not conducted.

-
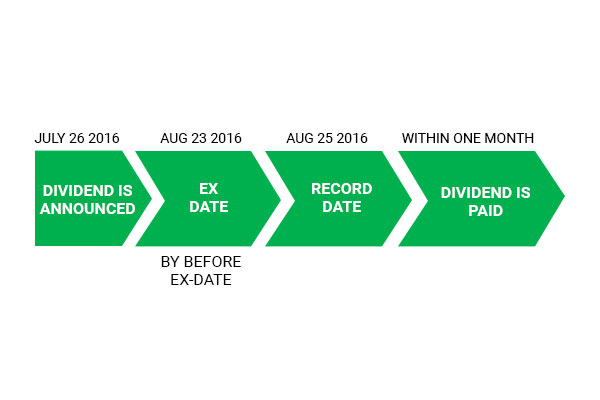
What is a Book-closure/Record date?
This is the cutoff date given by a company in order to determine which shareholders are eligible for corporate action benefits. It helps a company determine exactly who the shareholders of a company are on a given date. An investor must be listed as a holder of record to ensure the right to receive any type of corporate action.

-
What is a No-delivery period?
Whenever a company announces a book closure or record date, the exchange sets up a no-delivery period for that security. The transactions that have take place on the no delivery period are not rolled over for settlement on T+2 basis. This is done to ensure that investor's entitled for the benefit of corporate action is clearly determined. Usually the period between the Ex-date & Record date is the No-Delivery Period (ND Period)

-
What is an Ex- date?
The date from which a security begins to trade without the benefit of corporate action. If anybody buys a security on ex-date he will not be eligible for the benefit of corporate action.
For example, On July 26, 2015, Company X declares a dividend payable on September 10, 2015 to its shareholders. X also announces that shareholders of record on the company's books on or before August 10, 2015 are entitled to the dividend. The stock would then go ex-dividend usually two business days before the record date.
 Previous
Previous- Next
- /
- Take Test
-
Total Questions
10 -
Passing Marks
5 -
Total Time Allotted
Min -
Time Remaining
- Previous
- Next
- Submit Exam
