-
What is a Depository?
A depository is an institution that holds investor‘s securities in dematerialized/electronic form and facilitates transactions. One of the main functions of the depository is to transfer the ownership of the shares form one investor ’ s account to another investor's account whenever trade takes place. Depository is an institution that works like bank. Likewise our banks holds investor's funds, similarly depository holds securities (shares, debentures, mutual funds) in electronic form.

-
How is a depository similar to a bank?
A Depository can be compared with a bank, as bank hold funds in electronic form; in the same way Depository holds the financial instruments in electronic form.
Bank Depository Holds funds in an account Holds securities in an account Transfers funds between accounts on the instruction of the account holder Transfers securities between accounts on the instruction of the account holder Facilitates safe keeping of money Facilitates safe keeping of securities Facilitates transfers without having to handle physical money Facilitates transfers of ownership without having to handle physical securities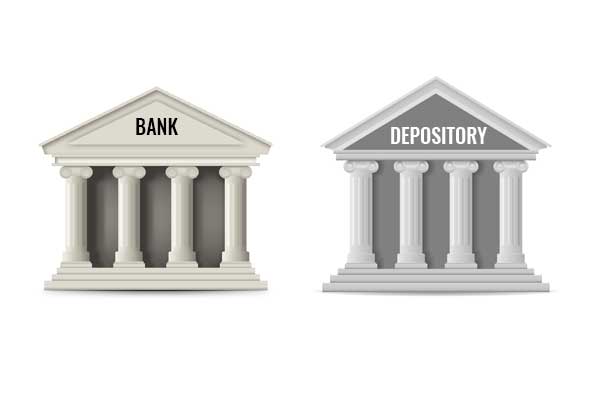 
-
Depositories in India?
There are two depositories in India:
- National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL) &
- Central Depository Services (India) Limited (CDSL).

-
What are the benefits of depository?
- Immediate transfer of securities
- No stamp duty on transfer of securities
- Elimination of risks associated with physical certificates such as bad delivery, fake securities, etc.
- Reduction in paperwork involved in transfer of securities
- Reduction in transaction cost
- Ease of nomination facility
- Change in address recorded with DP gets registered electronically with all companies in which investor holds securities eliminating the need to correspond with each of them separately
- Transmission of securities is done directly by the DP eliminating correspondence with companies
- Convenient method of consolidation of folios/accounts
- Holding investments in equity, debt instruments and Government securities in a single account; automatic credit into demat account, of shares, arising out of split/consolidation/merger etc.

-
Who is a Depository Participant (DP)?
The depository provides its services to investors through Depository participant (DP). According to SEBI regulations, amongst others, three categories of entities i.e. banks, financial institutions and SEBI registered trading members can be DPs. If you want to avail the services offered by the depository, you have to open an account with a DP. This is similar to opening an account with any branch of a bank.

-
How can one convert physical holding into electronic holding?
In order to dematerialize physical securities one has to fill in a Demat Request Form (DRF) which is available with the DP and submit the same along with physical certificates one wishes to dematerialize. Separate DRF has to be filled for each ISIN number.

-
What is Rematerialisation?
Securities which are in demat / electronic form can also be converted into physical form i.e. in the form of certificates. The process of converting electronic (demat) shares into physical form is called Rematerialisation.
The demat account holder has to submit a request to his/her DP which will check whether sufficient holding is available in the demat A/c for which rematerialisation request is given. The DP would generate the rematerialisation request and forward the same to respective share transfer agent (RTA) which would verify the request and if everything is ok, it would process & confirm the same. A new certificate would be printed and sent to the client directly by the RTA and the shares lying in the client's demat account will get extinguished.

-
Delivery Instruction Slip (DIS)
For transferring securities from one demat account to another demat account, a DIS is used. It is similar to a cheque in case we are doing any banking transaction.
There are two kinds of transfers which can be executed through a DIS. One type of transfer is called "Market Trade" another one is called "Off-Market Trade". A "Market Trade" is the transfer which is related to Stock Exchange i.e. if there is any buy or sale transaction through a stock broker, it is called market trade. Whereas, Off-Market Trades are transfers which are not related to any stock exchange. It is transfer between two individuals or entities such as gift, donation, transfer between accounts of the same holder, transfer between family members, charitable trust etc. All account holders have to sign the DIS.

-
Pledge & Hypothecation
Demat account holders can keep their electronic securities as collateral with a bank and take loan from them. The agreement between the client and the banker has to be outside the depository system.
The client who is taking the loan is called the "Pledgor" and the banker who is giving the loan is called the "Pledgee". Once the agreement is made between them, the client will give an instruction to the DP to initiate Pledge in favour of the bank. The securities will remain in the account of the client but will be blocked in favour of the Banker. Once the loan amount is re-paid by the client to the banker, the banker will close the pledge and the securities will be free. In case, the client does not repay the loan before the closure (agreed period of loan), the banker has the right to invoke the securities pledged. If an Invocation request is executed by the Banker's DP on instruction from Pledgee, the pledged securities lying in the client's demat account will get transferred to the banker's demat account. "Lock-in securities" can also be pledged however, invocation cannot be done on "Lock-in securities" till the Lock-in release date.

 Previous
Previous- Next
- /
- Take Test
-
Total Questions
10 -
Passing Marks
5 -
Total Time Allotted
Min -
Time Remaining
- Previous
- Next
- Submit Exam
